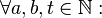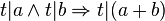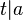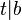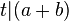Implikationen SoSe 2017: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus Geometrie-Wiki
*m.g.* (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→Implikationen) |
*m.g.* (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→Teilbarkeit durch 3) |
||
| Zeile 16: | Zeile 16: | ||
Die Aussage <math>a</math> heißt in der Implikation <math>a \Rightarrow b</math> Voraussetzung, die Aussage <math>b</math> wird Behauptung genannt. | Die Aussage <math>a</math> heißt in der Implikation <math>a \Rightarrow b</math> Voraussetzung, die Aussage <math>b</math> wird Behauptung genannt. | ||
==Beispiele== | ==Beispiele== | ||
| − | ===Teilbarkeit durch 3=== | + | ===Implikation 1: Teilbarkeit durch 3=== |
:Wenn die Quersumme <math>\overline{a}</math>einer natürlichen Zahl <math>a</math> durch <math>3</math> teilbar ist, dann ist auch die Zahl <math>a</math> durch <math>3</math> teilbar.<br /> | :Wenn die Quersumme <math>\overline{a}</math>einer natürlichen Zahl <math>a</math> durch <math>3</math> teilbar ist, dann ist auch die Zahl <math>a</math> durch <math>3</math> teilbar.<br /> | ||
:In Formelsprache: <math>\forall a \in \mathbb{N}: 3|\overline{a} \Rightarrow 3|a</math> | :In Formelsprache: <math>\forall a \in \mathbb{N}: 3|\overline{a} \Rightarrow 3|a</math> | ||
| − | + | *Voraussetzung: <math>3|\overline{a}</math> | |
| − | + | *Behauptung: <math>3|a</math> | |
| − | + | === Implikation 2: Teilbarkeit einer Summe=== | |
| + | :Für alle natürlichen Zahlen <math>a,b,t</math> gilt:<br /> | ||
| + | ::Wenn <math>t</math> die Zahlen <math>a</math> und <math>b</math> teilt, dann teilt <math>t</math> auch die Summe <math>a+b</math>. | ||
| + | :In Formelsprache: | ||
| + | :<math>\forall a,b,t \in \mathbb{N}:</math><br /> | ||
| + | ::<math>t|a \land t|b \Rightarrow t|(a+b)</math> | ||
| + | *Voraussetzung: Wir haben zwei Voraussetzungen die durch das logische und zu einer Voraussetzung zusammengefasst werden: | ||
| + | ::V<sub>1</sub>: <math>t|a</math> | ||
| + | ::V<sub>2</sub>: <math>t|b</math> | ||
| + | *Behauptung:<br /> | ||
| + | ::<math>t|(a+b)</math> | ||
<!--- Was hier drunter steht muss stehen bleiben ---> | <!--- Was hier drunter steht muss stehen bleiben ---> | ||
|} | |} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
[[Kategorie:Einführung_S]] | [[Kategorie:Einführung_S]] | ||
Version vom 10. Mai 2017, 15:45 Uhr
ImplikationenGenerelle Kennzeichnung von ImplikationenImplikationen sind spezielle mathematische Aussagen, deren Typ sich kurz als wie folgt darstellen bzw. beschreiben lässt:
Die Aussage BeispieleImplikation 1: Teilbarkeit durch 3
Implikation 2: Teilbarkeit einer Summe
|
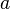 dann
dann 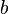 .
.
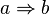
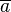 einer natürlichen Zahl
einer natürlichen Zahl 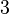 teilbar ist, dann ist auch die Zahl
teilbar ist, dann ist auch die Zahl 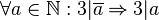
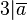
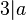
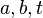 gilt:
gilt: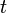 die Zahlen
die Zahlen 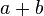 .
.