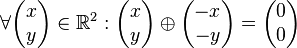Die abelsche Gruppe der geordneten Tripel reeller Zahlen 2012 13: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus Geometrie-Wiki
*m.g.* (Diskussion | Beiträge) (Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „<div style="margin:0; margin-right:4px; border:1px solid #27408B; padding: 1em 1em 1em 1em; background-color:#B9D0F0; align:left;"> {|width=90%| style="background…“) |
*m.g.* (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→Abgeschlossenheit der additiven Verknüpfung \oplusauf \mathbb{R}^2) |
||
| Zeile 9: | Zeile 9: | ||
<math>\forall \begin{pmatrix} x_1 \\ y_1 \\ z_1 \end{pmatrix}, \begin{pmatrix} x_2 \\ y_2 \\ z_2 \end{pmatrix} \in \mathbb{R}^3: \begin{pmatrix} x_1 \\ y_1 \\z_1 \end{pmatrix} \oplus \begin{pmatrix} x_2 \\ y_2 \\ z_2\end{pmatrix}= \begin{pmatrix} x_1+x_2 \\ y_1+y_2 \\ z_1 + z_2\end{pmatrix}\</math> | <math>\forall \begin{pmatrix} x_1 \\ y_1 \\ z_1 \end{pmatrix}, \begin{pmatrix} x_2 \\ y_2 \\ z_2 \end{pmatrix} \in \mathbb{R}^3: \begin{pmatrix} x_1 \\ y_1 \\z_1 \end{pmatrix} \oplus \begin{pmatrix} x_2 \\ y_2 \\ z_2\end{pmatrix}= \begin{pmatrix} x_1+x_2 \\ y_1+y_2 \\ z_1 + z_2\end{pmatrix}\</math> | ||
| − | =Abgeschlossenheit der additiven Verknüpfung <math>\oplus</math>auf <math>\mathbb{R}^ | + | =Abgeschlossenheit der additiven Verknüpfung <math>\oplus</math>auf <math>\mathbb{R}^3</math>= |
Folgt unmittelbar aus der Abgeschlossenheit der Addition auf <math>\mathbb{R}</math> | Folgt unmittelbar aus der Abgeschlossenheit der Addition auf <math>\mathbb{R}</math> | ||
| + | |||
=Die Assoziativität von <math>\oplus</math> auf <math>\mathbb{R}</math>= | =Die Assoziativität von <math>\oplus</math> auf <math>\mathbb{R}</math>= | ||
... Ergänzen Sie selbst. | ... Ergänzen Sie selbst. | ||
Version vom 12. Dezember 2012, 19:20 Uhr
Die nichtleere Menge
Die additive VerknüpfungFehler beim Parsen(Lexikalischer Fehler): \forall \begin{pmatrix} x_1 \\ y_1 \\ z_1 \end{pmatrix}, \begin{pmatrix} x_2 \\ y_2 \\ z_2 \end{pmatrix} \in \mathbb{R}^3: \begin{pmatrix} x_1 \\ y_1 \\z_1 \end{pmatrix} \oplus \begin{pmatrix} x_2 \\ y_2 \\ z_2\end{pmatrix}= \begin{pmatrix} x_1+x_2 \\ y_1+y_2 \\ z_1 + z_2\end{pmatrix}\
Abgeschlossenheit der additiven Verknüpfung
|
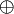 auf
auf 
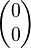 leistet das Verlangte. (Überzeugen Sie sich davon.)
leistet das Verlangte. (Überzeugen Sie sich davon.)