Lösung von Aufgabe 9.3P (SoSe 13): Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus Geometrie-Wiki
(table+) |
|||
| Zeile 34: | Zeile 34: | ||
<math>\angle ABC\ mit\ \ BA^{+}\ \cup\ \ BC^{+}\ </math> <math>mit\ A,B,C \in\ \epsilon</math><br /> | <math>\angle ABC\ mit\ \ BA^{+}\ \cup\ \ BC^{+}\ </math> <math>mit\ A,B,C \in\ \epsilon</math><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | '''Behauptung''': <math>\angle ABC\ \tilde {=}\ \angle A'B'C'</math> | + | '''Behauptung''': <math>\angle ABC\ \tilde {=}\ \angle A'B'C'</math><br /> |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable " | ||
| + | |- style="background: #DDFFDD;" | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | ! Beweisschritt | ||
| + | ! Begründung | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1) | ||
| + | | A' = Sg(A) | ||
| + | | Eigenschaft d. GS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2) | ||
| + | | B' = Sg(B) | ||
| + | | Eigenschaft d. GS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 3) | ||
| + | | C' = Sg(C) | ||
| + | | Eigenschaft d. GS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 4) | ||
| + | | <math>\\ BA^{+}\ \tilde {=}\ \ B'A'^{+}</math> | ||
| + | | (1); (2); Voraussetzung; Halbgeradentreue d. GS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 5) | ||
| + | | <math>\\ BC^{+}\ \tilde {=}\ \ B'C'^{+}</math> | ||
| + | | (2); (3); Voraussetzung; Halbgeradentreue d. GS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 6) | ||
| + | | <math>\left| \angle ABC\ \right|\ =\ \left| \angle A'B'C'\ \right| </math> | ||
| + | | (4); (5); Winkelmaßerhaltung d. GS; | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 7) | ||
| + | | <math>\angle ABC\ \tilde {=} \ \angle A'B'C' </math> | ||
| + | | (4); (5); (6); Winkelkongruenz | ||
| + | q.e.d. | ||
| + | |}--[[Benutzer:Nolessonlearned|Nolessonlearned]] 13:27, 15. Jul. 2013 (CEST)<br /> | ||
Version vom 15. Juli 2013, 13:27 Uhr
Beweisen Sie die Winkeltreue der Geradenspiegelung. Nutzen Sie für den Beweis die Halbgeradentreue und die Eigenschaft der Geradenspiegelung winkelmaßerhaltend zu sein.
| Voraussetzung | 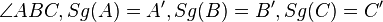
|
| Behauptung | 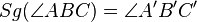
|
| Beweisschritt | Begründung |
|---|---|
1 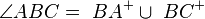 |
Voraussetzung, Def. Winkel |
2 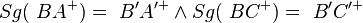 |
Halbgeradentreue, 1) |
3 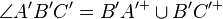 |
Def Winkel, 2) |
4 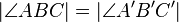 |
Winkelmaßerhaltend |
5 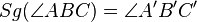 |
1)2)4) |
--Regenschirm 18:13, 25. Jun. 2013 (CEST)
Der Beweis ist korrekt.--Tutorin Anne 15:16, 26. Jun. 2013 (CEST)
Voraussetzung:
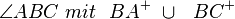
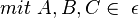
Behauptung: 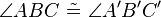
| Beweisschritt | Begründung | |
|---|---|---|
| 1) | A' = Sg(A) | Eigenschaft d. GS |
| 2) | B' = Sg(B) | Eigenschaft d. GS |
| 3) | C' = Sg(C) | Eigenschaft d. GS |
| 4) | Fehler beim Parsen(Syntaxfehler): \\ BA^{+}\ \tilde {=}\ \ B'A'^{+} | (1); (2); Voraussetzung; Halbgeradentreue d. GS |
| 5) | Fehler beim Parsen(Syntaxfehler): \\ BC^{+}\ \tilde {=}\ \ B'C'^{+} | (2); (3); Voraussetzung; Halbgeradentreue d. GS |
| 6) | 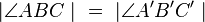
|
(4); (5); Winkelmaßerhaltung d. GS; |
| 7) | 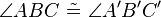
|
(4); (5); (6); Winkelkongruenz
q.e.d. |

