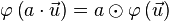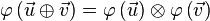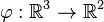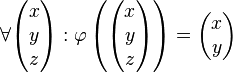Lineare Abbildungen, Vektorraumisomorphismus 2012 13: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus Geometrie-Wiki
*m.g.* (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→senkrechte Parallelprojektion) |
*m.g.* (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→senkrechte Parallelprojektion) |
||
| Zeile 9: | Zeile 9: | ||
==senkrechte Parallelprojektion== | ==senkrechte Parallelprojektion== | ||
<math>\varphi: \mathbb{R}^3 \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^2</math><br /> | <math>\varphi: \mathbb{R}^3 \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^2</math><br /> | ||
| − | <math>\forall \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{pmatrix}: \varphi \left( \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{pmatrix}\right)= \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \end{pmatrix}</math> | + | <math>\forall \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{pmatrix}: \varphi \left( \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{pmatrix}\right)= \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \end{pmatrix}</math><br /> |
| + | Man beweise: <math>\varphi</math> ist lineare Abbildung | ||
Version vom 12. Dezember 2012, 19:12 Uhr
DefinitionDefinition (lineare Abbildung) Beispielesenkrechte Parallelprojektion
|
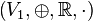 und
und 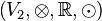 zwei Vektorräume über der Körper der reellen Zahlen.
zwei Vektorräume über der Körper der reellen Zahlen. 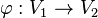 heißt lineare Abbildung wenn gilt:
heißt lineare Abbildung wenn gilt: 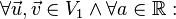
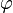 ist homogen:
ist homogen: