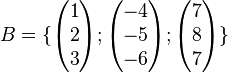Serie 06 12 13: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus Geometrie-Wiki
(→Aufgabe 6.2) |
(→Aufgabe 6.4) |
||
| Zeile 14: | Zeile 14: | ||
=Aufgabe 6.4= | =Aufgabe 6.4= | ||
| − | Bestimmen Sie die Koordinaten des Vekotrs <math>\vec{ | + | Bestimmen Sie die Koordinaten des Vekotrs <math> \vec{v}= \begin{pmatrix} 19 \\ 5 \\ -17 \end{pmatrix}</math> bezüglich der Basis <math>B=\{\begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{pmatrix};\begin{pmatrix} -4 \\ -5 \\ -6 \end{pmatrix};\begin{pmatrix} 7 \\ 8 \\ 7 \end{pmatrix}\}</math> |
| − | |||
<!--- hier drunter nichts eintragen ---> | <!--- hier drunter nichts eintragen ---> | ||
[[Kategorie:Linalg]] | [[Kategorie:Linalg]] | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 29. Januar 2014, 11:13 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis |
Aufgabe 6.1
Zeigen Sie, dass die Vektoren 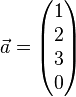 ,
, 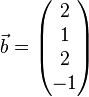 ,
, 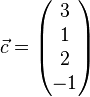 und
und 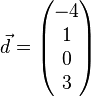 linear abhängig sind und überprüfen Sie, welche(r) der Vektoren sich als Linearkombination der jeweils anderen drei Vekotren darstellen lässt/lassen.
linear abhängig sind und überprüfen Sie, welche(r) der Vektoren sich als Linearkombination der jeweils anderen drei Vekotren darstellen lässt/lassen.
Aufgabe 6.2
Sei V ein reeler Vektorraum und 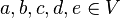 . Zeigen Sie, dass die folgenden Vektoren linear abgängig sind:
. Zeigen Sie, dass die folgenden Vektoren linear abgängig sind:
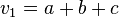 ,
, 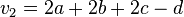 ,
, 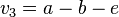 ,
, 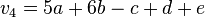 ,
, 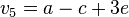 ,
, 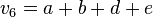
Aufgabe 6.3
Geben Sie für folgende Vektorräume eine Basis an:
a) 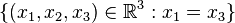
b)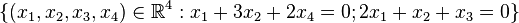
Aufgabe 6.4
Bestimmen Sie die Koordinaten des Vekotrs 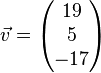 bezüglich der Basis
bezüglich der Basis