Lösung von Aufg. 10.2 S: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| Zeile 12: | Zeile 12: | ||
(1) <math>\exist M\in \overline{AB} : \left| AM \right| = \left| MB \right|</math> // (V2), Ex. & Eind. Mittelpkt. einer Strecke<br /> | (1) <math>\exist M\in \overline{AB} : \left| AM \right| = \left| MB \right|</math> // (V2), Ex. & Eind. Mittelpkt. einer Strecke<br /> | ||
| − | (2) <math>\exists m \in E : \ | + | (2) <math>\exists m \in E : \ M,P \in m</math> // (V1), (1), Axiom I.1<br /> |
(3) <math>\overline{MP} = \overline{MP}</math> // trivial<br /> | (3) <math>\overline{MP} = \overline{MP}</math> // trivial<br /> | ||
| − | (4) <math>\left | + | (4) <math>\left\overline{PA}\right \tilde {=} \left\overline{PB}\right</math> // (V3) <br /> |
| − | (5) <math>\left | + | (5) <math>\left\overline{AM}\right| \tilde {=} \left\overline{MB}\right</math> // (1) <br /> |
| − | (6) <math>\overline{AMP} | + | (6) <math>\overline{AMP} \tilde {=} \overline{BMP}</math> // (3-5), SSS <br /> |
| − | (7) <math>\angle AMP | + | (7) <math>\angle AMP \tilde {=} \angle BMP </math> // (6) <br /> |
(8) <math>\ m \perp \overline{AB}</math> // (7), Def. NW, Def. suppl., Supplementaxiom, Def. rechter Winkel, Def. senkrecht <br /> | (8) <math>\ m \perp \overline{AB}</math> // (7), Def. NW, Def. suppl., Supplementaxiom, Def. rechter Winkel, Def. senkrecht <br /> | ||
(9) <math>P \in m</math> also auch <math>P \in Mittelsenkrechte \overline{AB}</math> // (2)<br /> | (9) <math>P \in m</math> also auch <math>P \in Mittelsenkrechte \overline{AB}</math> // (2)<br /> | ||
Version vom 1. Juli 2012, 20:01 Uhr
Lösungsversuch Nummero6/Tchu Tcha Tcha:
Skizze:
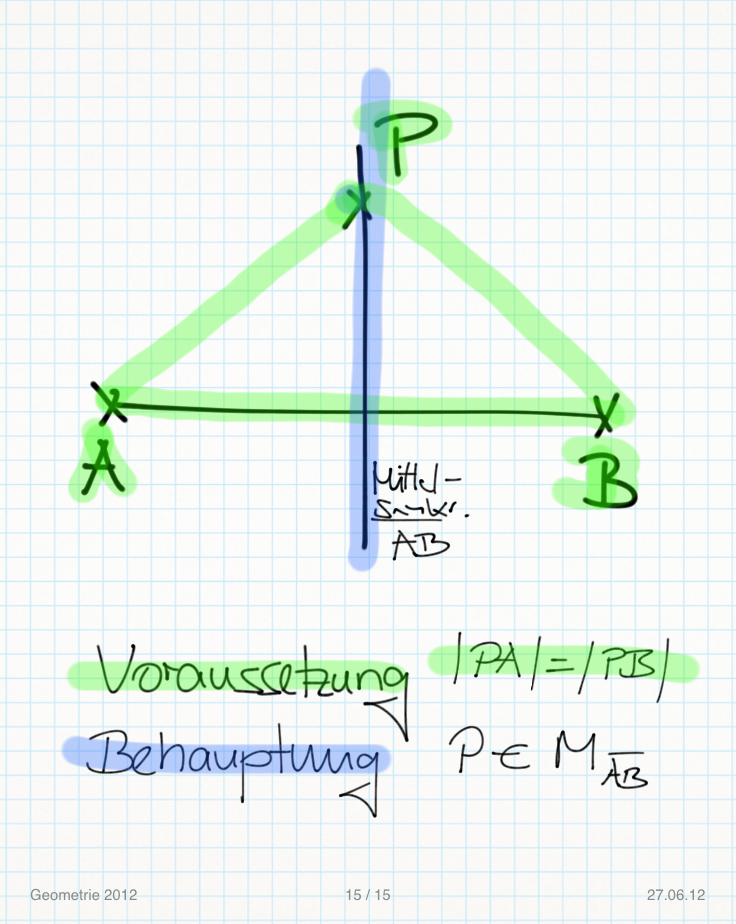
Voraussetzung:
(V1) Punkt P
(V2) Strecke 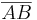
(V3) 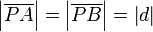
Behauptung:
P 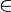 Mittelsenkrechte
Mittelsenkrechte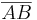
(1) 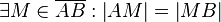 // (V2), Ex. & Eind. Mittelpkt. einer Strecke
// (V2), Ex. & Eind. Mittelpkt. einer Strecke
(2) 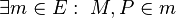 // (V1), (1), Axiom I.1
// (V1), (1), Axiom I.1
(3) 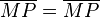 // trivial
// trivial
(4) Fehler beim Parsen(Syntaxfehler): \left\overline{PA}\right \tilde {=} \left\overline{PB}\right
// (V3)
(5) Fehler beim Parsen(Syntaxfehler): \left\overline{AM}\right| \tilde {=} \left\overline{MB}\right
// (1)
(6) 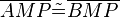 // (3-5), SSS
// (3-5), SSS
(7) 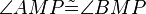 // (6)
// (6)
(8) 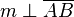 // (7), Def. NW, Def. suppl., Supplementaxiom, Def. rechter Winkel, Def. senkrecht
// (7), Def. NW, Def. suppl., Supplementaxiom, Def. rechter Winkel, Def. senkrecht
(9) 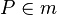 also auch
also auch 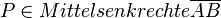 // (2)
// (2)
qed
--Tchu Tcha Tcha 18:58, 27. Jun. 2012 (CEST)
Kopernikus / Just noch ein sailA
Beweisen Sie Satz VII.6 a:
Wenn ein Punkt 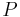 zu den Endpunkten der Strecke
zu den Endpunkten der Strecke 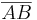 jeweils ein und denselben Abstand hat, so ist er ein Punkt der Mittelsenkrechten von
jeweils ein und denselben Abstand hat, so ist er ein Punkt der Mittelsenkrechten von 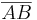 .
.
Vor:
1. 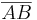
2. 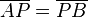
Beh:
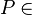 der Mittelsenkrechten von
der Mittelsenkrechten von 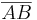
| Schritt | Beweis | Begründung |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 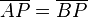
|
Vor. |
| 2 | 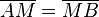
|
Ex. Eind. der Mittelsenkrechten von 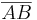
|
| 3 | 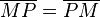
|
trivial |
| 4 | 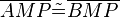
|
Kong. Satz SSS, 1,2,3 |
| 5 | 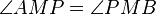
|
4, Dreieckskongruenz |
| 6 | 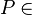 der Mittelsenkrechten von der Mittelsenkrechten von 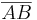
|
2,5, Def. VI.1 (Mittelsenkrechte) |
| 7 | Beh. stimmt q.e.d | 6, Beh. |
--Kopernikus 15:50, 28. Jun. 2012 (CEST)
--Just noch ein sailA 15:50, 28. Jun. 2012 (CEST)
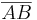
Lösungsversuch schokomuffin
Vor: Abstand PA = Abstand PB
Beh: 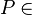 Mittelsenkrechte von
Mittelsenkrechte von 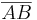
(1) 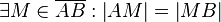 Ex. u. Eind. Mittelpunkt, Ax. II/ 2
Ex. u. Eind. Mittelpunkt, Ax. II/ 2
(2) 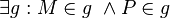 Ax. I/1
Ax. I/1
(3) 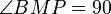 Ax. IV/2
Ax. IV/2
(4) 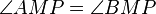 Def. RW, NW, (3)
Def. RW, NW, (3)
(5) 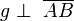 (4), (3)
(4), (3)
(6) g ist Mittelsenkrechte von 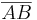 (4), (1)
(4), (1)
--schokomuffin 14:02 01. Jul. 2012 (CEST)

